
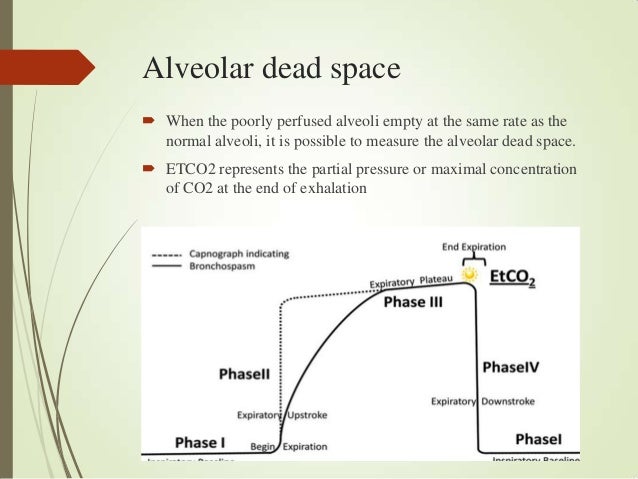
Generation 17 -23 is the respiratory zone where gas exchange occurs. In an average adult the volume of this space is about 150ml.įrom generation 17 onwards, small alveoli bud off the bronchi, these are where gas exchange takes place. The first 16 generations are termed the conducting zone, no bronchi in his region take part in gas exchange and this forms the anatomical dead space. The bronchi divide 23 times in total (23 generations) in order to increase the surface area available for gas exchange. It is lined with columnar ciliated epithelium and divides into the left and right major bronchi at the carina (T4). The larynx aids phonation and conducts the gas into the trachea which in an adult is about 18mm in diameter and 11 cm in length.
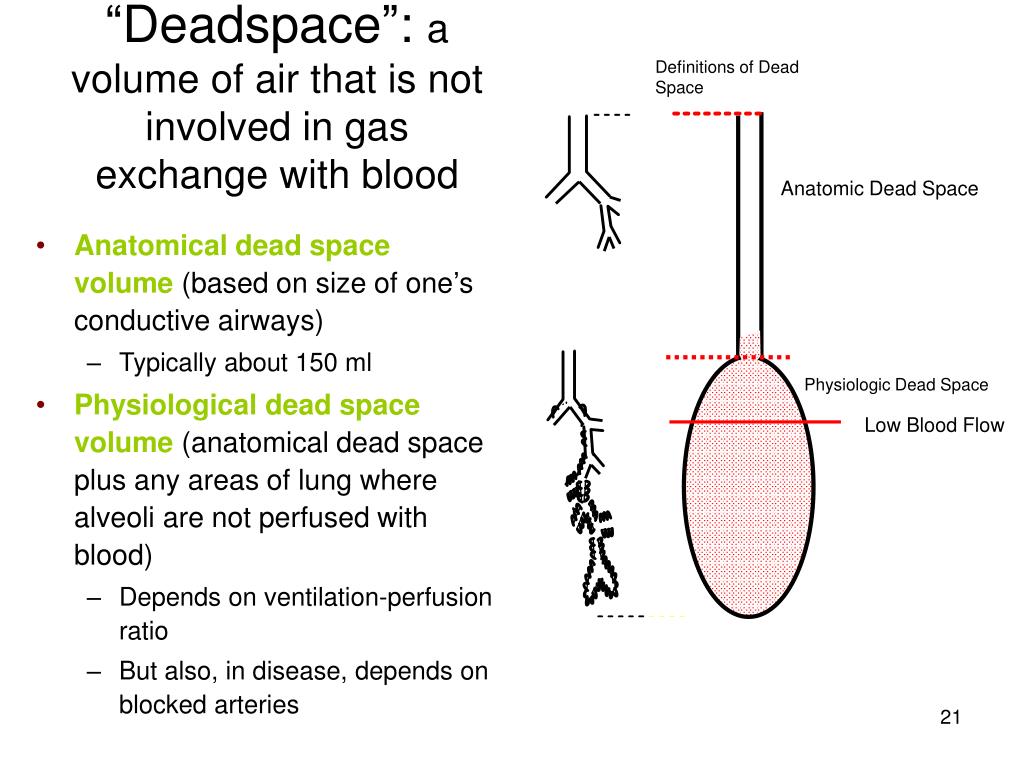
The nose, mouth and pharynx conduct air to the larynx, humidify and filter the air gases. To maintain gas exchange function, the anatomy of the respiratory system is designed in such a way to make the process as efficient as possible. A pressure-volume curve can be used for measuring:.production is reduced after a prolonged reduction in pulmonary blood flow.is the residual volume plus the inspiratory reserve volume.helium dilution over estimates FRC in patients’ with bullous lung disease.vital capacity is the volume of air expired from full inspiration to full expiration.the FRC in an average adult is 2.2litre.Fowlers method measures physiological dead space.The answers can be found at the end of the article, together with an explanation. Before continuing, try to answer the following questions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
